The Evolution of Mobile Technology : Mobile IoT is an excellent choice for global IoT. It is a team that refers to the 3GPP Standardised LPWA Technologies using licensed spectrum bands such as NB-IoT and LTE-M. LPWA Tecnologies using are networks designed for IoT applications that are low cost, use low data ranges require a long battery life and can operate in remote locations.
Connectivity is a crucial part of effective product design, and there the choice of connectivity technology and overall design must be considered early in the development process. The Evolution of Mobile Technology
Curious about the transformative power of IoT? Explore comprehensive section about IoT Technology.
Evolution of Cellular Networks
Mobile connectivity has evolved from being the infrastructure for human communication to telemetry, machine-to-machine and the internet of things applications. The Evolution of Mobile Technology
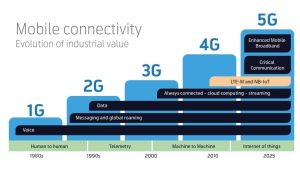
The mobile technology evolution from 1G to 4G and 5G
The first version of mobile connectivity- 1G – introduced wireless voice.
In 2G, roaming and SMS messaging were introduced and were later enhanced with GPRS for data communication. SMS messaging and GPRS become widely used for basic telemetry. Roaming made mobile technology suitable for deployments in multiple countries . The Evolution of Mobile Technology .Telenor was one of the first operators to offer M2M communications with things connected over the 2G network as early as the 1990s.
3G become a truly global standard and combined the best of competing technologies in a single standard. 3G evolutions were mainly centered around high speed data applications.
4G introduced LTE technology used for devices constantly connected to the internet. 4G answered the consumer need for bandwidth and speed and introduced a new way to handle voice, replacing 2G voice. The Evolution of Mobile Technology
LTE-M and NB – IoT Mobile IoT are especially designed for the internet of Things. LTE_M and NB-IoT support devices that need a long battery life and devices that need good network access in areas that are difficult to reach. The Evolution of Mobile Technology
5G networks use a combination of existing 4G LTE and new 5G New Radio %G NR technology. Today most networks that claim to be 5G networks are in fact using 4G LTE.
The Future of Mobile Technology
The mobile technology evolution from 1G to 4G is now continuing with 5G network which use a combination of existing 4G LTE and new 5G New Radio 5G NR technology. 4G and 5G have been designed to co-exist and applications designed for 4G, including LTE-M and NB-IoT, can be expected to have a very long life. The Evolution of Mobile Technology
5G enhances 4G in three main use case areas:
1. Enhanced mobile broadband
2. Critical communications
3. Mobile IoT

It also enables new IoT use cases that require high data volumes, for example streaming video. Critical Communications demand a much faster response and increased quality of service and security . 5G introduces 5G New Radio Technology which uses a higher radio frequency. At the same time as 5G starts to become available, operators are removing 2G networks from the market place so they can re-apportion the spectrum to other mobile Technologies .
What Is Mobile IoT Technology
With tens of billions of devices connected by 2025, the number of use cases will also accelerate rapidly, taking IoT into new markets. At the same time, connection types are diversifying to take account of the different needs of IoT devices. The cellular market has been on a journey from 1G to 5G and 5G is now available, alongside earlier cellular generations, to connect devices that require very high speed, very low latency as well as the capability to connect huge number of IoT devices in densely packed areas.
There are many different IoT connection types to choose from and there is likely to be an optimum solution for all IoT device types that matches IoT device requirements with the application, the system, software and devices it needs to connect to and which takes account of coverage and availability at the deployment location.

devices that need good network access in areas that are difficult to reach. These do not deliver the bandwidth of 5G but for many IoT use cases data rates and
latency are more than sufficient and low power consumption means IoT devices can have a long service life. The Evolution of Mobile Technology?